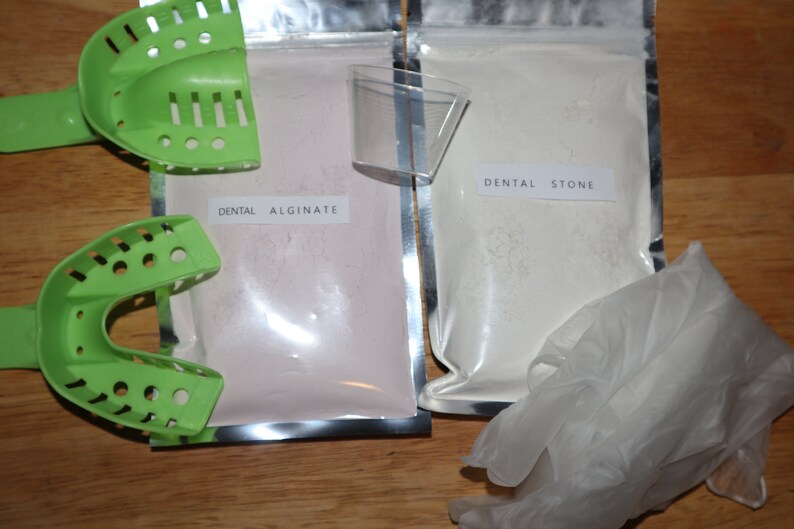


It was initially introduced in 1937, however it is not commonly used today (Sears, 1970).Īlginate on the other hand is an irreversible hydrocolloid. It has the ability to repeatedly pass between different viscosities simply by heating and cooling (Wassell, Barker and Walls, 2002).
ALGINATE IMPRESSION MATERIAL DENTAL FULL
Mucocompressive, good for full impressions with no flabby ridge Advantages: can reheat and impression retaken/modified.Setting time: altered with temperature of water, use cooler water for a shorter working time.Clinical use: primary impressions for complete dentures, border moulding/extension of trays.Either green used as greenstick for border moulding and tray extension or red used for complete dentures.Ĭompound for complete denture impressions requires heating to soften the compound before use. There are two main types of impression compound used in dentistry. Disadvantages: brittle, no recovery from deformation, excess saliva negatively effects detail replication.

Advantages: hydrophilic, good reproduction of details, good dimensional stability.Clinical use: occasionally for mucostatic impressions for flabby ridge.Plaster is an ideal mucostatic impression material however, its use has now been superseded by light bodied silicones and low viscosity alginate. These materials are rigid when set and therefore exhibit very little elasticity.ĭue to the rigidity of the materials any significant deformation to the impressions results in permanent deformation.
Table 1: Based on the classification of impression material by Wassell, Barker and Walls (2002) Non-elastic materials The ones in italics we will cover later in this article. Table 1 shows the various types of impression materials available and their classification. Of that, we can divide the elastic materials further into synthetic elastomers and hydrocolloids. We can categorise impression materials as non-elastic or elastic. Here we will look at the various types of impression materials encountered in general practice along with their uses, advantages and disadvantages. Impressions allow a straightforward method of obtaining an accurate replica of a patient’s teeth.

From restorative to orthodontics and much more. From study models for diagnosis and treatment planning to prosthodontics. Impression materials are encountered throughout various aspects of dentistry. In this month’s dental student’s guide, Hannah Hook explores the different types of impression materials and the pros and cons to each.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
